Cervical osteochondrosis or cervical osteochondrosis is a common disease among knowledge workers. The disease progresses rapidly. It is precisely with the development of cervical osteochondrosis and disc herniation that the incidence of early stroke has increased. For diagnosis, an MRI scan is required.
What is cervical osteochondrosis?
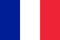
Cervical osteochondrosis is a common cause of neck pain, headache, pressure surge, shoulder pain, numbness of the fingers, and pain under the scapula. At present, with the increasing role of computers in our lives, the incidence of cervical osteochondrosis has increased significantly.
However, a fall or injury can stimulate the onset of osteochondrosis, and over time, the degeneration (wear and tear) of the intervertebral disc can cause symptoms.
symptom
In addition to moderate or mild pain, stiffness in the neck, and impaired mobility in some cases, many patients with cervical osteochondrosis experience numbness, tingling, or even tingling in the neck, arms, or shoulders due to chemicals. Powerless. Stimulate and squeeze cervical nerves.
For example, pinching the nerve roots of the C6-C7 segment can cause weakness in the triceps, shoulder or forearm muscles, weakness in the wrist muscles, resulting in "hanging" of the hand, and changes in the sensitivity of the middle finger.
Cervical osteochondrosis also often leads to spinal stenosis (narrowing) and other progressive diseases such as intervertebral hernia. How did this happen?
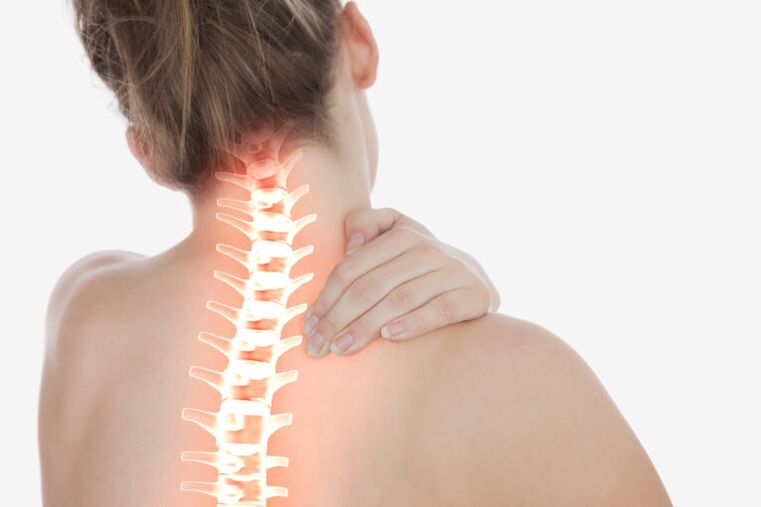
Osteochondrosis is nothing more than the degeneration of the spine structure, usually caused by the body's natural aging. As we age, ligaments thicken and bone hyperplasia appears on the vertebrae. When spinal ligaments thicken or bone hyperplasia occurs, and other reasons, the space in the spine becomes smaller. Spinal cord and nerves in the spinal canal. This condition is called stenosis, which is a narrowing of the spinal canal. Severe stenosis of the spinal canal can cause compression of the nerve roots and even the spinal cord itself.
In most cases, intervertebral hernia is also the result of degeneration. The intervertebral disc acts as a shock absorber for friction between the vertebrae, thereby preventing them from being destroyed. Over time, the intervertebral disc loses water and nutrients, flattens, becomes more fragile, and loses elasticity. As a result, a crack is formed in the ring, through which part of the nucleus pulposus is squeezed out into the spinal canal. This condition is called intervertebral hernia. If an intervertebral hernia compresses nearby nerve roots, pain syndromes and/or corresponding neurological symptoms will occur.
diagnosis
The successful diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis begins with a doctor's consultation. The doctor compiles the patient's medical history and performs a physical examination to check the mobility and sensitivity of the neck. During the examination, the patient may be asked to perform certain actions and report how the pain symptoms have changed (increased or decreased).
If the tests indicate that further tests are required, your doctor may recommend radiological tests, such as radiography, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computed tomography (CT). These diagnostic tests with varying degrees of reliability can confirm the presence and location of osteochondrosis, as well as identify other conditions that may cause the patient's symptoms (for example, calcification or arthritis).
At present, the best choice for radiological examination is MRI, because with the help of magnetic resonance imaging, not only high-quality detailed images of bone tissues (such as X-rays) can be obtained, but also spinal soft tissues (including muscles, ligaments, blood vessels, and blood vessels) can be obtained. High-quality detailed images of nerves and intervertebral discs. If there are any contraindications to MRI, CT is usually prescribed, which is mainly due to the presence of metal structures or devices in the body (artificial joints, pacemakers, etc. ). The quality of CT scans is lower than that of MRI scans, but they can also show the condition of the soft tissues of the spine.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
Conservative (non-surgical) treatment of osteochondrosis has always been recommended as the main strategy. Surgical intervention should only be considered when complex conservative treatment has not produced results for at least six months or when pain and other symptoms significantly interfere with the patient’s daily life. .
Methods for conservative treatment of cervical osteochondrosis may include:
- Spinal traction (traction). The recently used no-load method of spinal traction can completely eliminate the complications of this treatment method, and it cannot be done without load traction. As the intervertebral distance increases, the nutrition of all intervertebral discs improves, and the pain syndrome disappears.
- Corrective gymnastics. Corrective gymnastics can improve the mobility of spinal segments. In the movable vertebral segment, hernias and protrusions do not grow or form because the intervertebral disc performs its function.
- Massage therapy.
- medical treatement. Including NSAID (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) and painkillers. In most cases, medical treatment has little or no temporary effect.
- Neck corset, orthopedic pillows. They can be recommended to stabilize the cervical spine and reduce nerve root pressure after trauma and spinal fractures.
Surgical treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
If there is no obvious relief after six months of conservative treatment, and the patient's daily life becomes difficult, surgery can be considered. Usually, for cervical osteochondrosis, an operation called spinal fusion is performed to fix the affected vertebral segment. The surgery involves removing the intervertebral disc, decompressing the nerve roots, and placing bone or metal implants to maintain or create a normal intervertebral disc space and stabilize the spinal segment.
Usually, spinal fusion is performed on one vertebral body segment; in rare cases, surgery on two vertebral body segments may be considered. Nonetheless, patients need to know that surgery to relieve neck pain is unlikely to produce positive results compared to similar surgery to relieve arm pain in neck osteochondrosis. Therefore, if neck pain is the main or only symptom, spinal fusion can only be used as a last resort, or if all conservative treatments have been tried but failed. If it is not certain that the intervertebral disc space is the most likely source of neck pain, it is best to avoid surgery, even if conservative treatment does not significantly relieve the pain. In addition, don’t forget that spinal surgery can have serious consequences both in the surgical area (local infection, implant rejection, etc. ) and on the whole body (blood clots, drug allergic reactions, etc. ). ). Therefore, before deciding on the surgical treatment, it is necessary to discuss all the details of the operation directly with the surgeon who will perform the operation. It should also be noted that cervical spine surgery most often results in vertebral disability.
What is cervical osteochondrosis?
Official medicine interprets osteochondrosis as a degenerative dystrophy of the intervertebral disc.
In which part of the spine these discs are located, the definition of the disease is also given.
Let us specifically consider the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis, which accounts for almost 80% of all diseases of our back.
Sadly, the patients affected by this disease are between 30 and 50 years old, which is the golden age of working ability.
In young people, this disease is an independent disease. At older ages, it is already a pathology that has developed in the context of other joint diseases.
How does the disease develop?
For any part of the spine, the staged development of the disease is characteristic. Cervical osteochondrosis does not exceed this framework, so it is worth discussing each stage of it in detail.
- In the initial stage, the intervertebral disc is gradually destroyed. The annulus fibrosus is located between them, where cracks appear, which reduces the elasticity and strength of the intervertebral disc itself. They contract and compress nerve roots.
- The second stage is the result of the untreated first stage. The initial destruction of the intervertebral disc spread into a chronic form, tissue compaction occurred, and cervical dislocation was observed. Fall syndrome often develops at this stage.
- In the third stage, pain intensifies, persistent headaches, loss of sensitivity of the upper limbs, and "back pain" in the cervical spine suffer. This is because the fibrous annulus at this stage is almost completely destroyed.
Usually, the pain of third degree cervical osteochondrosis will be reduced. This happens at the moment when the cartilage tissue disappears without any damage.

reason
In view of the widespread prevalence of osteochondrosis, doctors began to study its causes closely. Many negative factors have been identified, but there is no clear list. The following has been announced so far:
- A sedentary lifestyle;
- Various poisonings and infections;
- A lot of physical activity;
- smokes;
- Constant weight lifting;
- Stress and nervousness;
- Uncomfortable shoes or irregular feet can cause unnecessary pressure on the spine;
- Improper nutrition;
- Frequent hypothermia and exposure to bad weather;
- Age-related changes;
- Spinal injury;
- Poor heritability;
- Strongly refuse to train if they have done so for a long time before then.
After familiarizing with the cause, it is obvious that cervical osteochondrosis may occur at any age. If the symptoms of osteochondrosis are not obvious at first and are characterized by rare pain, then over time, it turns out that the neck cannot be turned and the head cannot be tilted. These are not the only dangers of this disease.
What is the harm of the disease
Our neck is a great worker. She was involved all day long, her small vertebrae steadfastly withstood all our rotations and head tilts. If the bones are displaced, the nerves are squeezed, the blood vessels are compressed, and the vertebral artery that nourishes the brain will pass through the cervical spine. The arteries are compressed, the nerve roots are compressed, and the inflammatory process begins.

What will this cause? Spinal cord stroke, ischemia, intervertebral hernia-these are all serious consequences of cervical osteochondrosis. We have added here the general decline in mobility and osteophyte formation. As a result, our disability threatens to be completely unable to move. Faced with such a disappointing prognosis, it is important to quickly identify the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis.
symptom

The shortest way to identify osteochondrosis is the complaint of the patient. So, what does it feel like to talk about a person's cervical spine is destroyed? The picture of the disease looks like this:
- Dizziness;
- Strong headache
- Against the background of head pain, "flies" and colored spots appear in the eyes;
- Pain when turning or lifting weights;
- The pain radiates to other organs (heart area, other organs).
Sometimes signs of osteochondrosis can be attributed to other diseases, but they cannot be ignored, even if they are temporary.
Diagnosis and treatment
Based on the feelings expressed by patients, neurologists continue to make more accurate diagnoses of the disease. A few years ago, only X-rays could be used to identify osteochondrosis in the doctor's arsenal. Today, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are widely used. They allow you to accurately determine the stage of the disease.
After evaluating the generated pictures, a professional spinal neurologist will prescribe the necessary treatment plan. The first thing the doctor takes is pain relief, and then swelling and inflammation. To relieve pain, such anti-inflammatory drugs are used. As we remember, compression of the vertebral artery disrupts the supply of the brain, which means it needs to be improved. This is done with the help of muscle relaxants.

Knowing that the symptoms and treatment of cervical osteochondrosis are related to the spine, massage and physical therapy exercises must be included in measures to improve health. The massage is performed by the professional and the patient himself. There are also special exercises designed to develop the cervical spine and restore its mobility.